2017-2020年中国电动汽车充电站及充电桩市场研究报告

字数:13.0万页数:390图表数:305
中文电子版:9500元中文纸版:4750元中文(电子+纸)版:10000元
英文电子版:2500美元英文纸版:2700美元英文(电子+纸)版:2800美元
编号:jaf004发布日期:2017-03附件:下载
报告摘要
正文目录
图表目录
2016年汽车生产51.7万辆,同比增长51.7%。其中,纯电动乘用车生产26.3万辆,同比增长73.1%;插电式混合动力乘用车生产8.1万辆,同比增长29.9%;纯电动商用车生产15.4万辆,同比增长50.2%;插电式混合动力商用车生产1.8万辆,同比下降22.5%。2016年,2016年汽车产销分别完成2811.9万辆和2802.8万辆,占汽车总量的1.8%,较2015年提高4个百分点。2016年中国汽车保有量约100万辆,基本完成了中国《2012-2020年汽车发展规划》的阶段性目标,预计到2020年中国电动汽车销量将达211万辆,保有量超过500万辆。
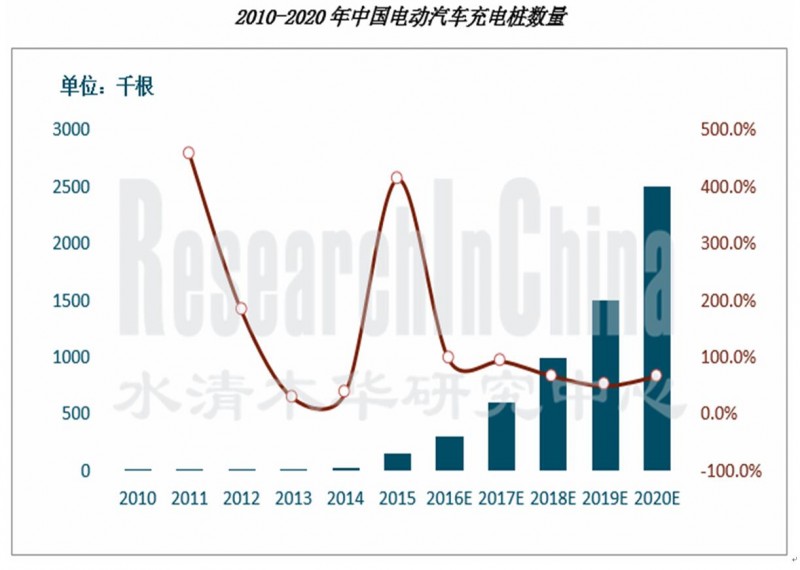
受汽车快速发展的推动,充电站和充电桩等配套设施,也迎来快速发展。2010年至2016年,中国充电站保有量从76座增长至5600座,年复合增长率达104.8%,公共充电桩数量从1122个增长至15万个,年复合增长率达126.1%。除了公共充电桩外,2016年全国私人居住地充电桩保有量在17万个左右,全国充电桩总量预计接近31万个。
从中国主要的推广城市的充电桩建设情况来看:
(1)截止到2016年,北京市累计建设充电站612座,公共+私人充电桩约6万个,其中公共管理平台接入运营商23家,接入并上线充电桩6000余根;已有5000余个小区安装了自用充电桩,总数达到2.6万个。同时,北京市住建委还配合国家电网完成了327个小区的充电条件改造。
(2)截至2016年底,上海共有城市公共快充站227座、高速公路快充站22座、公交充电站12座、储能公共快充站2座,充电桩总计5084台。
从产业政策方面,中国出台了《关于电动汽车用电价格政策有关问题的通知》、《关于汽车充电设施建设奖励的通知》、《关于“十三五”汽车充电设施奖励政策及加强汽车推广应用的通知(征求意见稿)》等一系列文件,鼓励充电桩建设,并且中央财政将拿出财政资金对充电桩建设运营良好的省市和企业进行补贴,激发全社会参与充电桩建设。
我国充电基础设施发展的目标是到2020年,建成集中充换电站1.2万座,分散充电桩480万个,满足全国500万辆电动汽车充电需求,原则上按照车桩比1:1的比例规划。从地区分布来看,中国已建成电动汽车充电站主要集中在华东、华北、华南等东部省市,其中,北京、上海、青岛等都是中国电动汽车充电站建设规模较大的城市。
国家鼓励充电基础设施政策发布后,各地纷纷加大投入力度建设充电桩,充电桩业务企业也纷纷宣布将在北上广布局数万充电桩。充电运营商、设备生产商、整体解决方案商,这三者是充电桩产业链条上的重要角色。充电桩产业主要存在三种商业模式,即:“充电桩+商品零售+服务消费”模式;“整车厂商+设备制造商+运营商+用户”模式;“充电APP+云服务+远程智能管理”模式。
水清木华研究中心《2016-2020年中国电动汽车充电站及充电桩市场研究报告》着重研究了以下内容:
![]() 汽车充电站、充电桩行业产业政策分析,包括未来5年汽车补贴政策、充电桩建设补贴和奖励政策、汽车推广计划、充电桩建设计划、充电基础电价及服务费政策等;
汽车充电站、充电桩行业产业政策分析,包括未来5年汽车补贴政策、充电桩建设补贴和奖励政策、汽车推广计划、充电桩建设计划、充电基础电价及服务费政策等;
![]() 全球和中国汽车发展现状,覆盖全球、美国、欧洲、日本和中国等主要市场产销数据,中国对乘用车、客车、物流车等汽车现状及趋势进行了分析预测;
全球和中国汽车发展现状,覆盖全球、美国、欧洲、日本和中国等主要市场产销数据,中国对乘用车、客车、物流车等汽车现状及趋势进行了分析预测;
![]() 全球充电桩发展特点,覆盖了全球主要国家充电桩补贴政策,对美国SAE、欧洲ICE、日本CHAdeMO、中国GB/T等充电接口标准进行了深入分析,并对主流的充电设备及运营商进行了分析;
全球充电桩发展特点,覆盖了全球主要国家充电桩补贴政策,对美国SAE、欧洲ICE、日本CHAdeMO、中国GB/T等充电接口标准进行了深入分析,并对主流的充电设备及运营商进行了分析;
![]() 中国汽车充电站、充电桩行业发展情况分析,对未来5年充电桩建设计划进行了分析预测,着重分析了充电桩盈利模式、众筹模式、以及汽车用户的驾驶习惯和充电行为分析等;
中国汽车充电站、充电桩行业发展情况分析,对未来5年充电桩建设计划进行了分析预测,着重分析了充电桩盈利模式、众筹模式、以及汽车用户的驾驶习惯和充电行为分析等;
![]() 30个多主要省市充电桩截至2016年底的建设现状,未来的建设计划等;
30个多主要省市充电桩截至2016年底的建设现状,未来的建设计划等;
![]() 全球及中国13家充电运营商分析(运营模式、盈利模式、APP、合作企业等)等;
全球及中国13家充电运营商分析(运营模式、盈利模式、APP、合作企业等)等;
![]() 中国8家汽车充电设备供应商企业经营状况及发展战略分析等;
中国8家汽车充电设备供应商企业经营状况及发展战略分析等;
![]() 中国主要整车厂商在充电领域的战略布局,以及与充电设备供应商和充电运营商的合作。
中国主要整车厂商在充电领域的战略布局,以及与充电设备供应商和充电运营商的合作。
Chinaproduced 517,000 new energy vehicles in 2016, surging by 51.7% from a year earlier, including 263,000 battery-electric passenger vehicles, soaring 73.1% year on year, and 81,000 plug-in hybrid passenger vehicles, up 29.9%, 154,000 battery-electric commercial vehicles, rising by 50.2% year on year, and 18,000 plug-in hybrid commercial vehicles, decreasing by 22.5% year on year. In 2016, new energy vehicles made up 1.8% ofChina’s total production and sales of vehicles (output: 28.119 million units, sales: 28.028 million units), an increase of four percentage points from a year ago. New energy vehicle ownership approximated 1 million units inChinain 2016, basically accomplishing phased target of the Planning for the Development of New Energy Vehicle during 2012-2020. It is expected that EV sales will reach 2.11 million units in 2020 with EV ownership exceeding 5 million units.
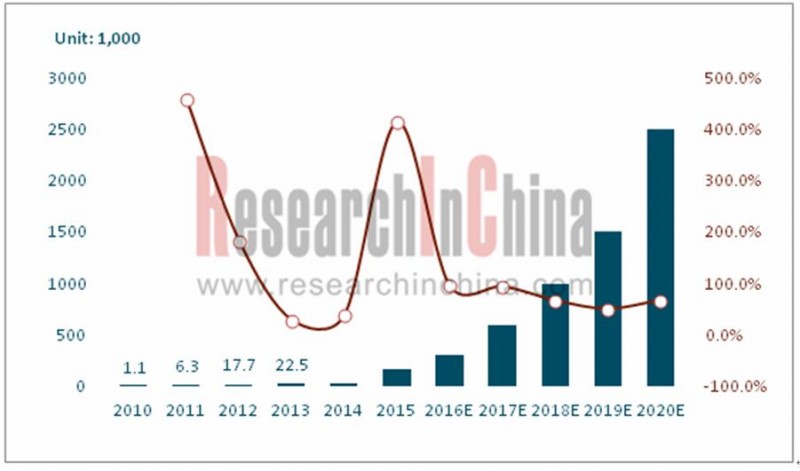
Driven by rapid development of new energy vehicles, the supporting facilities like charging station and charging pile also flourish. Charging station ownership inChinaincreased from76 in2010 to5,600 in2016 at a CAGR of 104.8%. The number of public charging piles grew from 1,122 to 150,000 at a CAGR of 126.1% during the same period. In addition to public charging piles, private charging pile ownership reached about 170,000 units in 2016, thus bringing the country’s total number of charging piles up to nearly 310,000.
The construction of charging piles in major cities that promote new energy vehicles inChinais as follows:
(1) By the end of 2016,Beijinghas built 612 charging stations and approximately 60,000 charging piles (public +private). In particular, 23 charging operators are accessed onto public management platform and more than 6,000 charging piles are available; and 5,000 communities or more have installed a total of 26,000 self-use charging piles. Additionally, Beijing Municipal Commission of Housing and Urban-Rural Development collaborated with State Grid to finish altering the charging conditions in 327 communities.
(2) By the end of 2016,Shanghaihas built 227 pubic fast charging stations, 22 fast charging stations on expressways, 12 bus charging stations, 2 public charging stations for energy storage, and a total number of 5,084 charging piles.
As to industrial policies, China introduced a series of documents, such as the Circular on Issues Related to the Policy on Price of Electricity Used by EVs, the Circular on Rewarding the Construction of New Energy Vehicle Charging Facilities, and the Circular on Incentive Policies on New Energy Vehicle Charging Facilities and Strengthening the Popularization and Application of New Energy Vehicles during the 13th Five-year Plan Period (Exposure Draft), encouraging the construction of charging piles and allocating central fiscal funds to subsidize the provinces and enterprises which construct and operate charging piles in a sound way so as to stimulate enthusiasm of the society to participate in the construction of charging piles.
Chinaaims to build 12,000 centralized charging/battery swap stations and 4.8 million scattered charging piles across the country by 2020 to meet charging demand of 5 million EVs in principle of 1 vehicle to 1 charging pile. Regionally, the EV charging stations that have been built are primarily concentrated in eastern provinces in East China, North China, and South China, of whichBeijing,Shanghai, andQingdaoare the cities with massive construction of EV charging stations inChina.
With introduction of incentive policies on charging facilities, all parts of the countries have ramped up their efforts to build charging piles, and the companies that run charging pile business also announce to build tens of thousands of charging piles in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou. Operators of charging facilities, manufacturers of equipment, and providers of integrated solutions are three major roles in charging pile industry chain. There are three main business models in charging pile industry: “charging pile + commodity retail + service consumption”, “carmakers + equipment manufacturers + operators + users”, and “charging APP + cloud services + remote intelligent management”.
Number of EV Charging Piles inChina, 2010-2020E
China EV Charging Station and Charging Pile Market Report, 2016-2020 by ResearchInChina highlights the following:
![]() Industrial policies on car charging station/pile, including
policies on subsidies for new energy vehicles, policies on subsidies and
rewards for construction of charging piles, the planning for promotion of new
energy vehicles, the planning for construction of charging piles, policies on
basic electricity tariff of charging and service charges over the next five
years;
Industrial policies on car charging station/pile, including
policies on subsidies for new energy vehicles, policies on subsidies and
rewards for construction of charging piles, the planning for promotion of new
energy vehicles, the planning for construction of charging piles, policies on
basic electricity tariff of charging and service charges over the next five
years;
![]() Development status of new energy vehicles around the world
and inChina, including
output and sales data in major markets (global,USA,
Europe,Japan, andChina), and status quo & trends of new
energy vehicles (passenger vehicles, buses, logistic vehicles) inChina;
Development status of new energy vehicles around the world
and inChina, including
output and sales data in major markets (global,USA,
Europe,Japan, andChina), and status quo & trends of new
energy vehicles (passenger vehicles, buses, logistic vehicles) inChina;
![]() Development characteristics of charging pile globally,
covering policies on subsidies for charging pile in major countries, in-depth
analysis of charging port standards (America’s SAE, Europe’s ICE, Japan’s
CHAdeMO, and China’s GB/T), and study of mainstream charging equipment and
operators;
Development characteristics of charging pile globally,
covering policies on subsidies for charging pile in major countries, in-depth
analysis of charging port standards (America’s SAE, Europe’s ICE, Japan’s
CHAdeMO, and China’s GB/T), and study of mainstream charging equipment and
operators;
![]() Development of car charging station/pile industry in China,
including analysis of 5-year planning for construction of charging pile,
particularly profit models and crowdfunding models of charging pile, and
driving habits and charging behaviors of new energy vehicle users;
Development of car charging station/pile industry in China,
including analysis of 5-year planning for construction of charging pile,
particularly profit models and crowdfunding models of charging pile, and
driving habits and charging behaviors of new energy vehicle users;
![]() Construction of charging piles in more than 30 provinces and
cities by the end of 2016 and construction plans
Construction of charging piles in more than 30 provinces and
cities by the end of 2016 and construction plans
![]() 13 global and Chinese charging operators (operating models,
profit models, APP, partners);
13 global and Chinese charging operators (operating models,
profit models, APP, partners);
![]() Operation and development
strategies of 8 Chinese suppliers of car charging equipment;
Operation and development
strategies of 8 Chinese suppliers of car charging equipment;
![]() Major Chinese carmakers’ strategic layout in charging field
and cooperation with charging equipment suppliers and charging operators.
Major Chinese carmakers’ strategic layout in charging field
and cooperation with charging equipment suppliers and charging operators.





 扫一扫关注微信
扫一扫关注微信